
As the back-to-school season kicks off, many families are turning their attention to one of the most significant financial challenges they will face: paying for college. With tuition costs continuing to climb, it's crucial to have a well-thought-out savings strategy in place. This article will explore various college savings options, detailing their benefits and drawbacks, and offer insights into why early planning is essential for maximizing your savings.
The Rising Cost of College
The cost of college education has been steadily increasing for decades, outpacing inflation and putting a strain on family budgets. According to the
National Center for Education Statistics
, the average cost of tuition and fees for the 2022-2023 academic year was $14,688 for all institutions (including 2 and 4 year colleges), and $34,923 at private colleges. These figures don't even account for room, board, books, and other expenses, which can add thousands more to the total cost. Given these numbers, it's no surprise that families are looking for the best ways to save for their children's education.
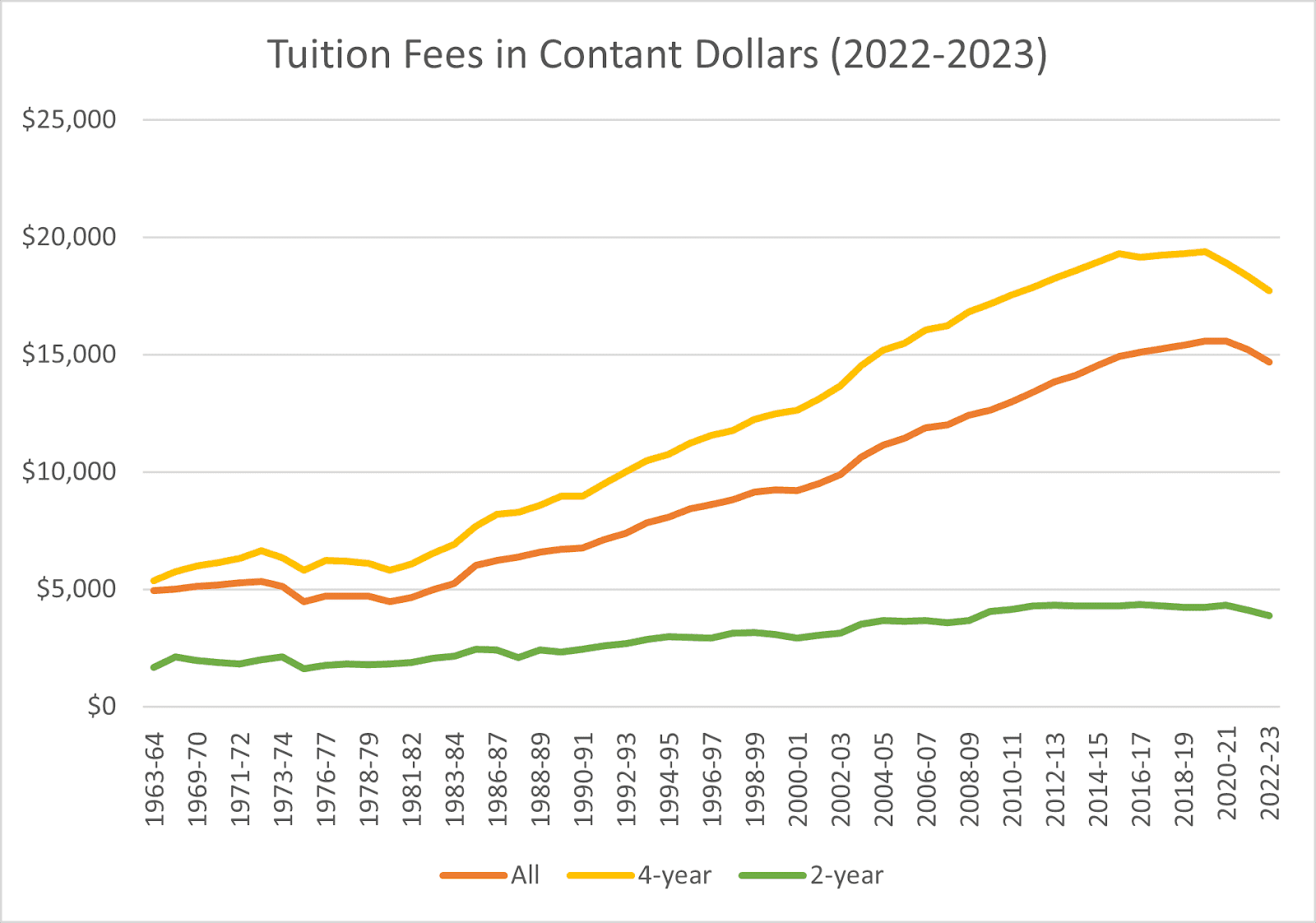
SOURCE National Center for Education Statistics
Understanding FAFSA
The FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) is a critical form that students complete to determine their eligibility for federal financial aid for college. The information provided on the FAFSA, including family income and assets, helps calculate the Expected Family Contribution (EFC), which is used by colleges to determine financial aid packages. Assets such as savings accounts, investments, and other financial resources can impact the EFC and, consequently, the amount of aid a student is eligible to receive. However, not all assets are treated equally; for instance, retirement accounts and the family home are typically not counted, but savings, checking accounts, and certain investments may reduce the amount of aid offered. Understanding how assets are factored into the FAFSA can help families better plan for college expenses.
Once you've gained a clear understanding of how FAFSA works and how your assets impact financial aid eligibility, it's time to explore broader college financial planning options. By combining federal aid with other resources such as scholarships, grants, and savings plans like 529 accounts, you can create a comprehensive strategy to manage college expenses. Careful planning and informed decisions now will help minimize student loan debt and set the stage for long-term financial success. Here we explore the pros and cons of the two of the most used college financing plans.

College Savings Plans: A Targeted Approach
One of the most popular options for college savings is the 529 College Savings Plan. This plan is specifically designed to help families save for future education costs. Depending on the state, there are other options.
Pros:
- Tax-Free Growth: Perhaps the most significant advantage of a 529 plan is that earnings grow tax-free. As long as the withdrawals are used for qualified education expenses, they won't be taxed, allowing your investment to grow faster than it would in a taxable account.
- Flexible Withdrawal Options: 529 plans cover a wide range of educational expenses, including tuition, fees, books, supplies, and even room and board. Some plans also allow for the funds to be used for K-12 education, two-year colleges, trade schools, and student loan repayments. Be sure to look at the details for each plan to understand the restrictions prior to investing.
- Potential ROTH IRA Conversion: A new provision allows for the conversion of leftover 529 funds into a ROTH IRA, providing a safety net if your child doesn't need all the money for college. There is a lifetime limit of $35,000.
- Tuition Lock-In: Some states offer prepaid college savings plans that let you lock in today's tuition rates, protecting you from future increases.
- Covers Various Educational Expenses: Beyond tuition, these plans can also cover mandatory fees, books, supplies, and sometimes even computers if they are required by the school.
Cons:
- Penalties for Non-Educational Use: If you withdraw money for non-qualified expenses, a penalty will be assessed on the earnings, fees may apply, along with having to pay federal income tax.
- Restrictions on College Eligibility:
529 plans are limited to accredited institutions. If your child decides to attend a non-eligible school, the funds might not be usable without penalties.

Other Savings and Investment Plans: Flexibility and Control
For families looking for more flexibility, other savings and investment plans might be a better fit. These options include traditional savings accounts, brokerage accounts, and custodial accounts under the Uniform Transfers to Minors Act (UTMA) or Uniform Gifts to Minors Act (UGMA).
Pros:
- Flexibility: Unlike 529 plans, these accounts aren't limited to educational expenses. This flexibility can be advantageous if your child decides not to attend college or needs the funds for other purposes, such as starting a business or buying a home.
- Control Over Assets: With a standard brokerage account, you have full control over how the funds are invested. You can choose from a wide range of assets, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, tailoring the investment strategy to your risk tolerance and financial goals.
- No Geographic or Purpose Restrictions: These accounts aren't tied to specific uses or locations, meaning the funds can be used anywhere in the world and for any purpose.
Cons:
- Taxable Income: Unlike 529 plans, earnings in these accounts are subject to taxes at your current income level, which can diminish your overall return. The "kiddie tax" rules also apply to minors' accounts, which could result in higher tax liabilities.
- No Tuition Breaks: Unlike prepaid college savings plans, these accounts don't offer any protection against rising tuition costs. You'll have to pay whatever the rate is at the time your child enrolls.
- Control Over Assets:
Having full control over a standard brokerage account can be challenging as it can expose you to higher market risks, and demands significant time for management.

Why Early Planning is Crucial
The power of compound interest cannot be overstated when it comes to college savings. The earlier you start saving, the more time your money has to grow. For example, if you start saving $200 a month when your child is born, and you earn an average annual return of 6%, you could have over $77,000 saved by the time your child turns 18. If you wait until your child is 10 to start saving, you'll need to set aside about $740 a month to reach the same goal.
Early planning also allows you to explore all available options and make informed decisions. You can adjust your savings strategy as your financial situation evolves, ensuring that you're on track to meet your goals.

Next Step: Personalized College Savings Plans
Navigating the complexities of college savings can be overwhelming, but you don't have to do it alone. For more detailed information on these and other college savings options, visit our webpage. Better yet, schedule a consultation with me to create a personalized plan tailored to your family's unique needs and financial situation. Together, we can develop a strategy to help you prepare for the costs of higher education.
College planning is one of the most important financial steps you can take for your child's future. With the right approach, you can ensure that your child's educational dreams become a reality without compromising your financial security. Let's start planning today!
Contact Us
Check the background of your financial professional on FINRA's BrokerCheck.
The content is developed from sources believed to be providing accurate information. The information in this material is not intended as tax or legal advice. Please consult legal or tax professionals for specific information regarding your individual situation. Some of this material was developed and produced by FMG Suite to provide information on a topic that may be of interest. FMG Suite is not affiliated with the named representative, broker - dealer, state - or SEC - registered investment advisory firm. The opinions expressed and material provided are for general information, and should not be considered a solicitation for the purchase or sale of any security.
We take protecting your data and privacy very seriously. As of January 1, 2020 the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) suggests the following link as an extra measure to safeguard your data: Do not sell my personal information.
Financial Professionals associated with this site are registered to conduct securities business and licensed to conduct insurance business in certain states. Response to, or contact with, residents of other states will be made only upon compliance with applicable licensing and registration requirements. The information in this website is for U.S. residents only and does not constitute an offer to sell, or a solicitation of an offer to purchase brokerage services to persons outside of the United States.
Securities and investment advisory services offered through NEXT Financial Group, Inc., Member FINRA/SIPC. T Wyman & Associates & Wyman Financial Solutions are not affiliated with NEXT Financial Group, Inc.
All Rights Reserved | Wyman Financial Group
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use | Powered by Levitate
